Trash (deleted records)
It is possible to access previously deleted records in the "Trash" section. Ended executions are automatically moved to trash after a configurable timeout and subsequently permanently deleted after a configurable timeout.
If not configured otherwise, per default, ended executions will be moved to trash after 2 weeks. Trashed executions will remain in trash for another 2 weeks before being permanently deleted from the Engine database.
Trashing Execution records is executed asynchronously!
Therefore, Execution records may still exist after the delete() method returns.
Concept
Whether a record is in trash is marked by the is_deleted flag. Ended executions are automatically marked as deleted after a timeout. Manually trashing a record will mark it as deleted. Records which are marked as deleted can be restored. After a timeout deleted records are permanently deleted from the database.
Configuration
The behaviour can be configured using the Workspace Configuration. Please refer to Trash for configuration options.
Moving Records to trash
Moving a project to trash will also trash all records of that project.
Via the User-Interface
Moving Individual Records to trash
Open the record and click on "Move to trash" in the "More Actions" popover.
The move to trash action in the more actions popover
The record will be moved to the "Trash" section.
Bulk-Move-to-trash many Records
Open the workspace dashboard, project dashboard, or execution live monitor. In the resources list check the records and click on "Move to trash" in the "More Actions" popover.
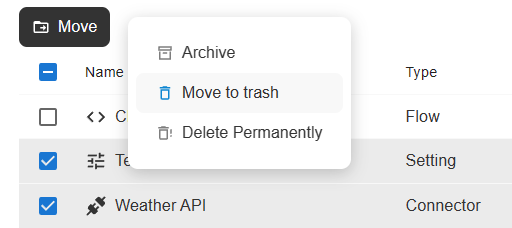
The bulk-move-to-trash action in the more actions popover
The records will be moved to the "Trash" section.
Via the Flow-API
Use the delete method on any record.
Trash a setting.
import flow_api
def handler(system: flow_api.System, this: flow_api.Execution, inputs: dict):
system.setting('the-setting').delete()
return this.success('all done')
Via the REST-API
Make a HTTP DELETE request.
Trash a setting
curl -X DELETE https://your-workspace-name.cloudomation.com/api/latest/setting/the-setting?by=name
Permanently Deleting Records
Permanently deleting a record from Engine is permanent. The record cannot be restored afterwards!
Permanently deleting a project will also permanently delete all records of that project.
Handling errors when permanently deleting records
Permanently deleting a record that is used by another record (e.g. a setting that is used by a schedule) is not possible and will fail with the following error message:
Failed to delete or update <resource-type>, <resource-name>:
The row is still in use by table <resource-type-of-other-resource>
To permanently delete the aforementioned record, you need to either permanently delete the record that uses it (e.g. permanently delete the schedule first to permanently delete the setting) or make sure that the record is not used by other records (e.g. remove the setting from the schedule).
The following might cause this issue:
- settings used in schedules
- schedulers used in schedules
- flows used in schedules
- flows used in webhooks
- object templates used in custom objects
Permanently deleting projects
You might encounter above error when you permanently delete a project. This happens because, when permanently deleting a project, all it's resources are permanently deleted as well. The order in which they are permanently deleted is, however, not fixed. This can lead to the issue described above (when a record that is still used by another record cannot be permanently deleted).
To circumvent this, you can first permanently delete all schedules and webhook in the project. After this, you can permanently delete the project.
Via the User-Interface
Permanently Deleting Individual Records
Open the record and click on "Delete Permanently" in the "More Actions" popover.
The delete permanently action in the more actions popover
Bulk-Permanently-Delete many Records
Open the workspace dashboard, project dashboard, or execution live monitor. In the resoures list check the records and click on "Delete Permanently" in the "More Actions" popover.
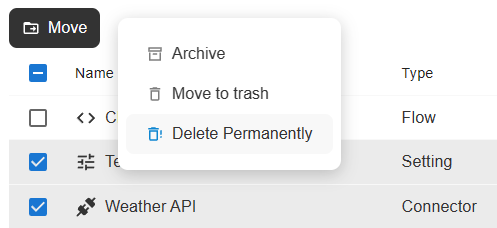
The bulk-delete-permanently action in the more actions popover
Via the Flow-API
Use the delete method with the permanently=True argument on any record.
Permanently delete a setting.
import flow_api
def handler(system: flow_api.System, this: flow_api.Execution, inputs: dict):
system.setting('the-setting').delete(permanently=True)
return this.success('all done')
Via the REST-API
Make a HTTP DELETE request.
Permanently delete a setting
curl -X DELETE https://your-workspace-name.cloudomation.com/api/latest/setting/the-setting?by=name\&permanently=true
Accessing Records in Trash
Via the User-Interface
List Resources in Trash
Resources in Trash are listed in the "Trash" section at the bottom of the left-hand navigation.
List Activities in Trash
Activities in Trash can be listed using the advanced search. Please refer to Advanced Search for details.
Access Records in Trash
Clicking on a record in the "Trash" section or the advanced search will open it. Opened records in the trash are marked with a badge.
The in trash badge
Records in trash cannot be modified and all actions are disabled, except "Delete permanently" and "Restore".
Via the Flow-API
List Records in Trash
Listing methods can be configured to access records in trash. To include records in trash in the listing the allow_deleted argument must be set to True.
List all settings in Trash.
import flow_api
def handler(system: flow_api.System, this: flow_api.Execution, inputs: dict):
for setting in system.settings(
# do not include "Normal" (not deleted) records in the lising
allow_normal=False,
allow_deleted=True,
):
this.log(setting.get_dict('name', 'deleted_at'))
return this.success('all done')
Access Records in Trash
Individual records in trash can be accessed using the Flow-API. The allow_deleted argument must be set to True.
Read value of a setting in trash.
import flow_api
def handler(system: flow_api.System, this: flow_api.Execution, inputs: dict):
value = system.setting(
'the-deleted-setting',
allow_deleted=True,
).get('value')
this.log(value=value)
return this.success('all done')
Trying to access records in trash without using the allow_deleted flag will result in a PermissionDeniedError:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "example-read-deleted-with-permission-error (4c886cf9-61cc-41ab-b3a2-c6fdad5a334c)", line 4, in handler
flow_api.exceptions.PermissionDenied: {"operation": "read", "by": "name", "ids": ["the-deleted-setting"], "table": "setting", "message": "No permission to read setting in project 239dface-c437-488f-9390-42c70483c3b6 with name(s) {'the-deleted-setting'}: Cannot access deleted record without `allow_deleted` flag.", "reason": "Cannot access deleted record without `allow_deleted` flag."}
Via the REST-API
List Records in Trash
Use the allow_deleted flag with any listing request.
List only settings in trash.
curl https://your-workspace-name.cloudomation.com/api/latest/setting?allow_normal=false\&allow_deleted=true
Please refer to Accessing and Manipulating Records for details on how to use the REST API.
Access records in Trash
Use the allow_deleted flag.
Access a setting in trash.
curl https://your-workspace-name.cloudomation.com/api/latest/setting/the-deleted-setting?by=name\&allow_deleted=true
Restoring Records
Restoring a project will also restore all records of that project.
Via the User-Interface
Restoring Individual Records
Open a record from the "Trash" section and click on "Restore" in the "More Actions" popover.
The restore action in the more actions popover
The record will be restored and moved to the project it is associated with.
Bulk-Restore many Records
Open the "Trash" section. In the list check the records and click on "Restore".
The bulk-restore action
The records will be restored and moved to the projects they are associated with.
Via the Flow-API
Use the restore method on any record.
To be able to access a record which is in trash the allow_deleted argument must be used.
Restore a setting.
import flow_api
def handler(system: flow_api.System, this: flow_api.Execution, inputs: dict):
system.setting('the-deleted-setting', allow_deleted=True).restore()
return this.success('all done')
Via the REST-API
Make a HTTP PATCH request to restore.
Restore a setting
curl -X PATCH https://your-workspace-name.cloudomation.com/api/latest/setting/the-deleted-setting/restore?by=name\&allow_deleted=true