Retries
Using retries it is possible to define fault-tolerant automations.
Use Cases
Use retries
- When certain parts of your automation occasionally fail and the failure is temporary.
- To poll a system until it reaches a certain status.
Concept
The retry feature is implemented as a Wrapper.
Importing the Wrapper bundle will provide you with a wrapper called retry.
When the retry wrapper is attached to a connector, it will monitor the execution status of the connection and restart the execution in case an error occurs.
As all wrappers, the retry wrapper can be statically attached and configured. Please refer to Static Wrappers for more information.
Alternatively, the retry wrapper can be dynamically attached and configured. Please refer to Dynamic Wrappers for more information.
The most common usage is to dynamically attach and configure the retry wrapper to a connector. This way the configuration of the retries is individual to the particular use of the connector.
The retry wrapper provided by Engine is considered an example which can be extended or modified to your needs.
Parameters
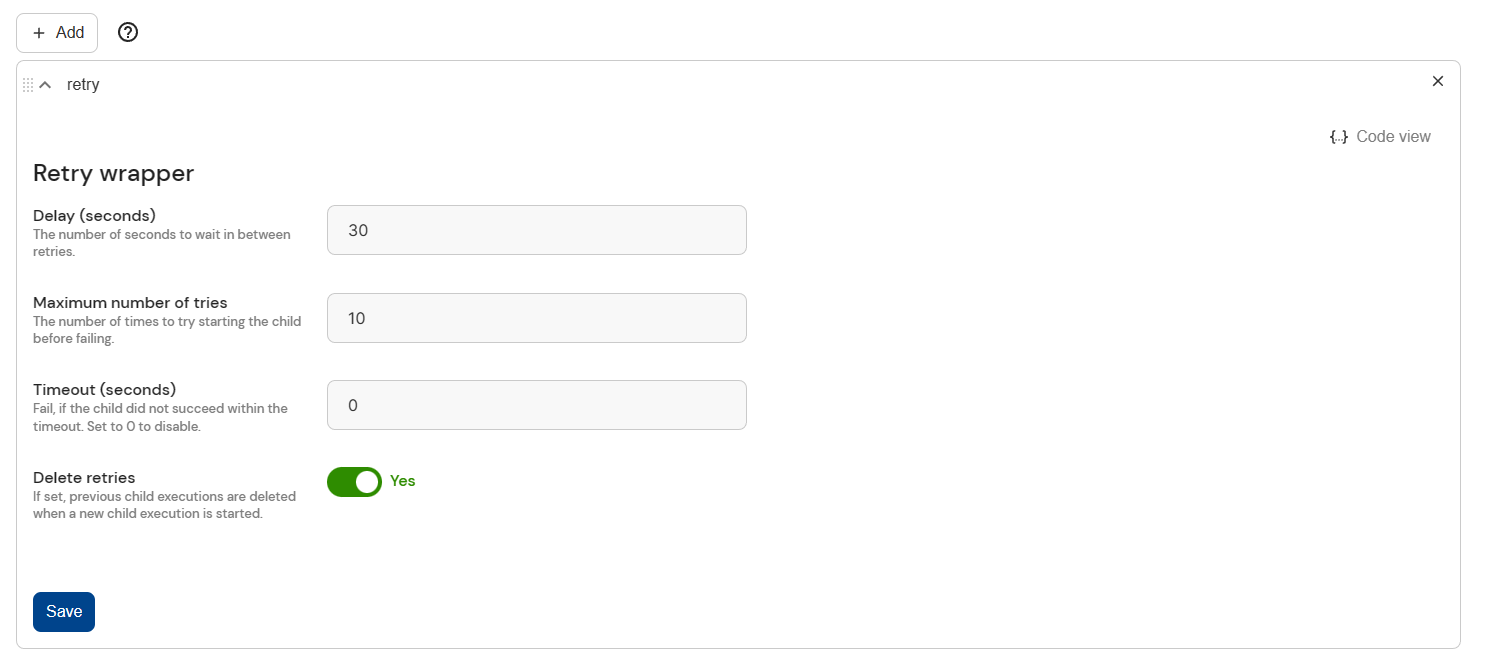
Refer to the retry wrapper for its parameters.
The parameters can be configured in code or, if you use a static wrapper, with the help of a form.
Examples
Using a connection with retries
import flow_api
def handler(system: flow_api.System, this: flow_api.Execution, inputs: dict):
# We want to try to connect to <name-of-a-connector>.
# There are a maximum of 10 attempts. If an attempt fails,
# we'll wait 30 seconds until retrying.
this.using(
'retry',
max_tries=10,
delay_sec=30,
).connect('<name-of-a-connector>')
return this.success('all done')
Alternatively, you can use a static wrapper. This is useful if a resource should always be wrapped. Here's how the above example would look like as a static wrapper: